SSTP Guide¶
Introduction¶
About this Document¶
In this guide, we explain the basic principles of SSTP and how to deploy the AXS Guard SSTP server in your network. This document is intended for technical personnel and network administators.
Examples used in this Guide¶
All setups and configuration examples in this guide are executed as an advanced administrator. Some options are not available if you log in as a full administrator or a user with lower access privileges.
As software development and documentation are ongoing processes, the screenshots shown in this guide may slightly deviate from the current user interface.
Basic SSTP Concepts¶
About¶
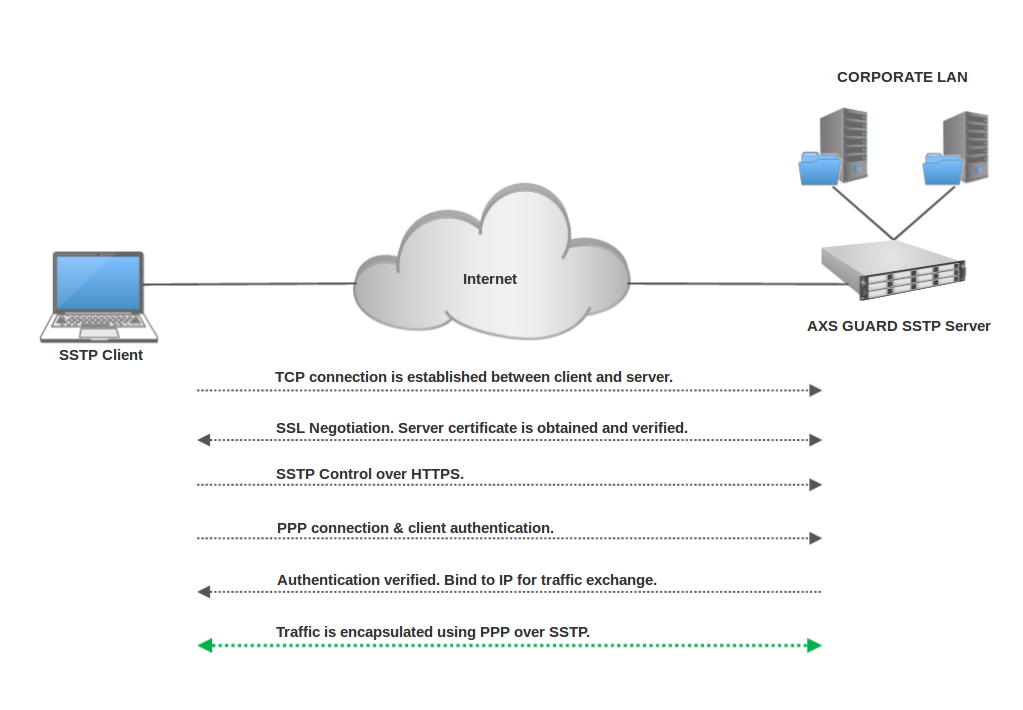
The Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) provides a mechanism to transport PPP traffic through an SSL/TLS channel. SSL/TLS provides transport-level security with key negotiation, encryption and traffic integrity checking.
SSTP servers must be authenticated during the SSL/TLS phase. SSTP clients can optionally be authenticated during the SSL/TLS phase and must be authenticated in the PPP phase. The use of PPP allows support for common authentication methods, such as EAP-TLS and MS-CHAP.
The SSTP server uses TCP port 443 by default, allowing SSTP traffic to pass through virtually all firewalls and proxy servers, except for authenticated web proxies.
PKI¶
It is recommended that the SSL certificate used for SSTP be issued by a public Certification Authority (CA).
You can also use a certificate signed by the AXS Guard CA for this purpose, but this requires additional configuration. The CA certificate must be exported and added as a trusted root CA on each Windows client in order for SSTP connections to succeed. A configuration example is provided in this manual.
Proxy ARP¶
If the client’s PPP interface has an IP address in a different IP range than the LAN of the SSTP server, standard routing applies.
If the client’s PPP interface has an IP address in the same IP range as the secure LAN of the SSTP server, traffic can only be routed correctly by using Proxy ARP.
Proxy ARP is a technique in which a host, usually a router, answers ARP requests intended for another host by supplying its own physical address. By "pretending" to be another host, the AXS Guard appliance automatically routes the traffic back to the requesting host. Proxy ARP is defined per RFC 1027. For more information about ARP, see the appropriate online resources.
Port Sharing¶
SSTP uses TCP port 443 by default, allowing clients to pass through virtually all firewalls and proxy servers, except for authenticated web proxies.
The AXS Guard reverse proxy manages the SSTP server as a separate application, so system administrators can share the same external IP address and port with other applications and services in the corporate network.
Firewall & Authentication¶
Server-side¶
It is highly recommended to configure the AXS Guard firewall so that only required network resources can be accessed by SSTP clients. This also improves security in case a client is infected with malware or hijacked.
The system default firewall policies block all access by default. System administrators should configure the appropriate firewall policies at the group or user level.
The AXS Guard appliance also provides strong authentication methods to verify the identity of users. These methods are intrinsically stringent enough to ensure the security of the SSTP server by withstanding any attacks it is likely to encounter. A configuration example is provided in this manual.
Client-side¶
The following authentication protocols are supported on the client side:
-
Secured password (EAP-MSCHAP v2) with encryption enabled
-
MS-CHAP v2
Ensure to enable data encryption when setting up the connection on your
Windows client (select Require encryption - disconnect if server declines).
Important
CHAP is not supported and will terminate the PPP link prematurely if enabled.
Routing¶
VPNs have two main routing modes:
-
Full tunnel mode: All network traffic is routed through the VPN, including Internet traffic.
-
Split tunnel mode: Only network traffic for specific ranges is sent through the VPN.
The Windows SSTP client operates in full tunnel mode by default. This allows system administrators to monitor and control traffic within the corporate network more effectively, e.g. by means of a filtering proxy or a firewall.
This default behavior can be changed, as explained in the section called setting up routing.
SSTP Server Configuration¶
Configuration Overview¶
The following steps are required to successfully configure the AXS Guard SSTP server and will be explained in this chapter:
-
Enable the SSTP VPN feature
-
Import or generate an SSTP server certificate
-
Configure the SSTP server settings
-
Enable SSTP for users and groups who need access to the service
-
Configure the SSTP firewall and application control policies
-
Configure the authentication policy for SSTP users
Feature Activation¶
-
Log in to your appliance.
-
Go to System > Feature Activation.
-
Enable the SSTP server feature.
Choosing a Server Certificate¶
-
Go to PKI > Certificates.
-
Import a certificate signed by a public CA or use the AXS Guard CA to issue a server certificate as shown below.
Server Configuration¶
-
Go to VPN > SSTP > Server.
-
Configure the SSTP server settings as explained below.
-
Save or update your configuration.
Enabling the Server¶
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
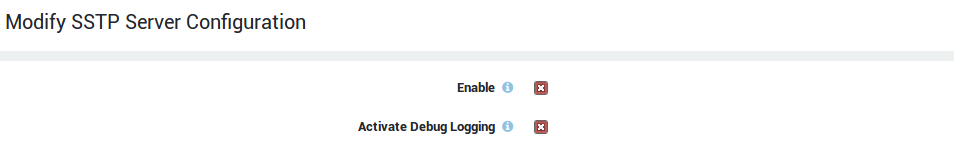
Enable |
Enables and starts the SSTP server. Ensure that no other service is using the configured TCP port, otherwise the service will fail to start. |
Activate Debug Logging |
Activate debug logging, which includes additional information for advanced administrators and developers to debug software issues. |
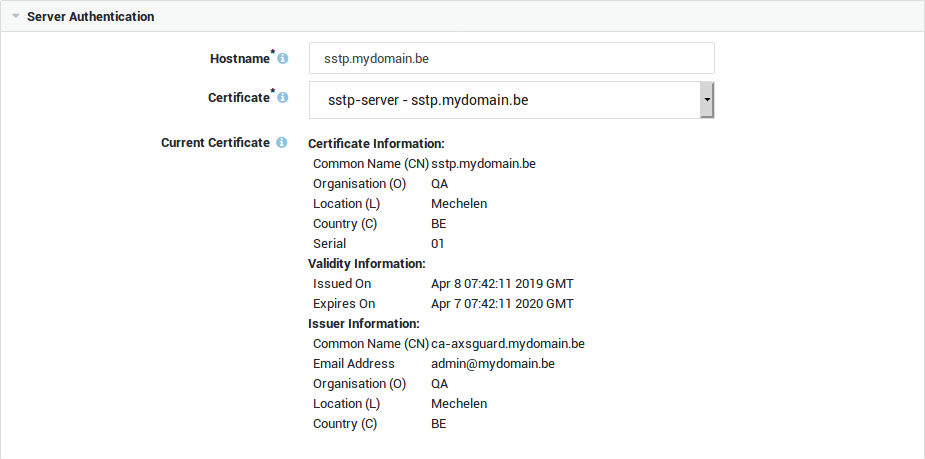
Server Authentication¶
The AXS Guard CA certificate must be added as a trusted root CA on each Windows client for SSTP connections to succeed. This is not required when using a server certificate issued by a public CA.
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
Hostname |
Hostname as used by the clients to connect to the SSTP VPN server. It must match the name as configured in your public DNS record(s) as well as the CN (or one of the Subject Alternative Names) in the server certificate. |
Certificate |
Select the server certificate for the SSTP server. Go to PKI ▸ Certificates to create or import a server certificate. It is recommended that the SSL certificate used for SSTP be issued by a public Certification Authority (CA). You can also use a certificate signed by the AXS GUARD CA for this purpose, but this requires additional configuration. The CA certificate must be exported and added on each Windows client as a trusted root CA in order for SSTP connections to succeed. |
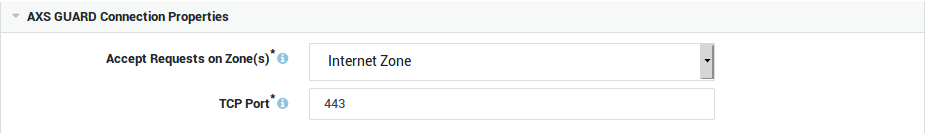
Connection Properties¶
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
Accept Requests on Zone(s) |
Select the zone(s) on which client requests are accepted. The SSTP server will listen on all IP addresses that have been configured for the selected zone(s). The Custom Zone option allows you to define your own zone. |
Accept Requests on Interface(s) |
Select the appropriate Internet and/or DMZ interfaces. This field only appears if you selected "Custom Zone". |
Accept Requests on IP Address(es) |
Enter one or multiple public IP addresses. This allows you to restrict connections to specific IPs, rather than allowing connections to an entire zone. This field only appears if you selected "Custom Zone". |
TCP Port |
Enter the external port to be used by Internet clients. SSTP uses TCP port 443 by default – the same port used by HTTPS traffic. |
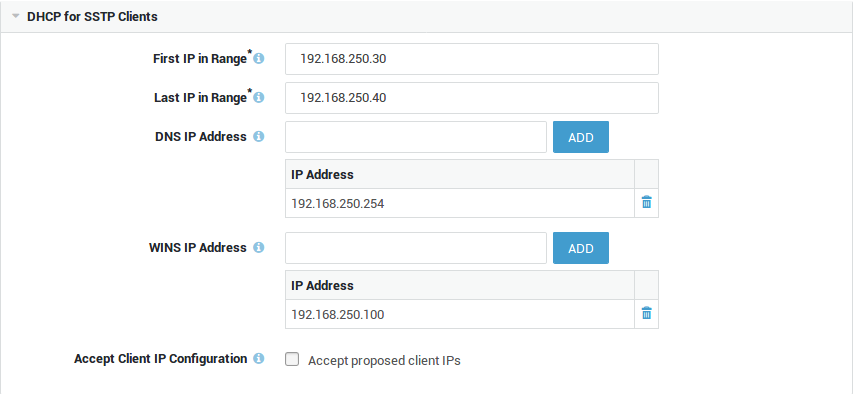
DHCP Settings¶
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
First IP in Range |
The first IP address in the IP address pool that is reserved for SSTP clients. The IP range may be a subrange of the secure LAN IP range, in which case ARP proxying is used. Proxy ARP is a technique in which a host, usually a router, answers ARP requests intended for another host by supplying its own physical address. By "pretending" to be another host, the AXS GUARD appliance appliance correctly routes the traffic back to the requesting host. Proxy ARP is defined per RFC 1027. |
Last IP in Range |
The last IP in the address pool to be reserved for SSTP clients. |
DNS IP Address |
Specify the DNS server(s) to be used by the remote SSTP client. This is usually the secure LAN IP of the AXS GUARD appliance or the IP address of your primary Domain Controller. |
WINS IP Address |
Specify the WINS server(s) to be used by the remote SSTP client. WINS stands for Windows Internet Naming Service and is Microsoft’s implementation of DNS. Note: The AXS GUARD appliance cannot be used as a WINS server. |
Accept Client IP Configuration |
Check this option to accept the IP address proposed by the SSTP client. Sometimes clients need a specific IP to be able to use certain applications in your network. Accepting a remote client IP also allows a SSTP client to print documents via an RDP Session if the drivers for printer sharing are installed on the client. |
Inactivity Settings¶
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
Idle Timeout |
SSTP will terminate the connection after a period of inactivity. The link is considered idle when no data is sent or received. The default value is set to |
Granting Access to SSTP¶
Users must be granted access to the SSTP service before they can use it.
Group-based Access¶
-
Go to Users&Groups > Groups.
-
Select the appropriate group.
-
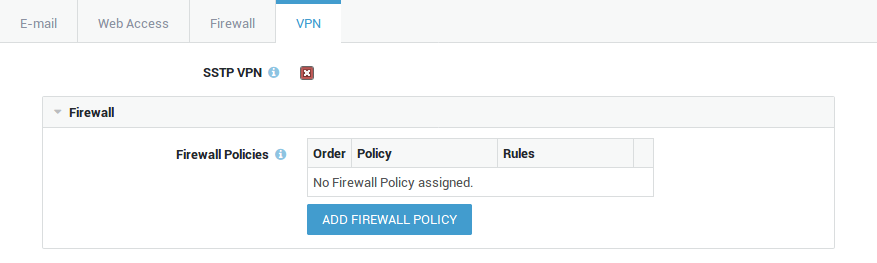
Select the VPN tab and make sure the SSTP VPN option is checked.
User-based Access¶
-
Go to Users&Groups > Users.
-
Select the appropriate user.
-
Select the VPN tab and make sure the SSTP VPN option is checked.
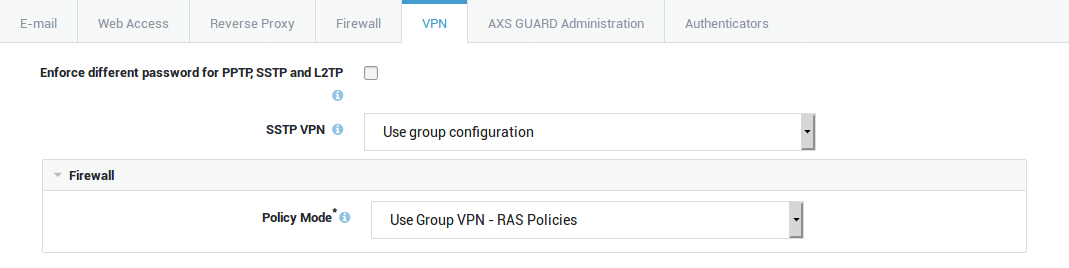
Firewall and Application Control Settings¶
About Application Control
The application control system monitors the application layer (layer 7 of the OSI model) of the network. This is also known to as Deep Packet Inspection (DPI), a form of computer network packet filtering that examines the data part of a packet as it passes the AXS Guard, searching for defined criteria, such as protocols or websites, to decide whether the packet may pass or needs to be blocked. The AXS Guard also collects and reports statistical information about all layer 7 traffic.
The application control system allows application-layer detection of protocols, regardless of the port being used. This means that it is possible to both detect known protocols on non-standard ports, e.g. http traffic on ports other than 80, and also the opposite, e.g. detect Skype traffic on port 80. The system will also detect and block access to certain file types, such as multimedia files (if enabled).
Group-based Configuration¶
-
Navigate to Users & Groups > Groups.
-
Click on the appropriate group name.
-
Select the VPN tab to specify the VPN firewall and application control policies.
-
Update your configuration.
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
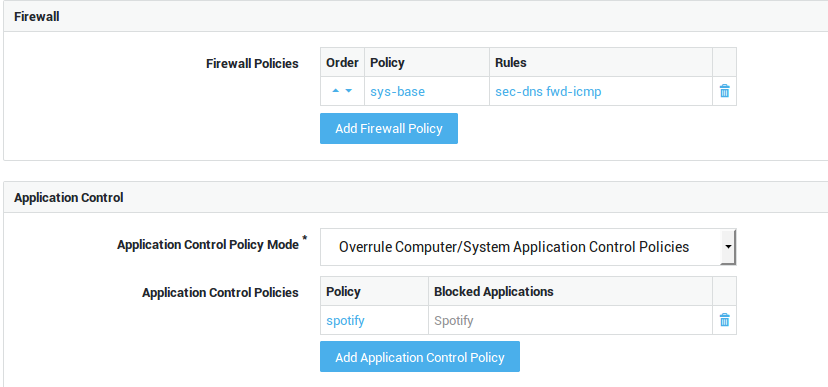
Add Firewall Policy |
Select specific firewall policies for group members who connect to the corporate network with a VPN client, such as a PPTP client. Go to Firewall > Policies > Dynamic for an overview of defined firewall policies. |
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
Use computer/system application control policies |
Enforce the system-wide policies, assigned under Application Control > General and the computer-level policies, if any. |
Add to computer/system application control policies |
Assign specific policies to this group, in addition to the system-wide policies configured under Application Control > General and computer-level policies, if any. |
Overrule computer/system application control policies |
Do not enforce the system-wide policies and computer-level policies, but only the specified policies. The specific policies will be enforced when a member of the group successfully authenticates. |
User-based Configuration¶
-
Navigate to Users & Groups > Users.
-
Click on the appropriate username.
-
Select the VPN tab and select the appropriate firewall and application control policy modes as explained below.
-
Update your configuration.
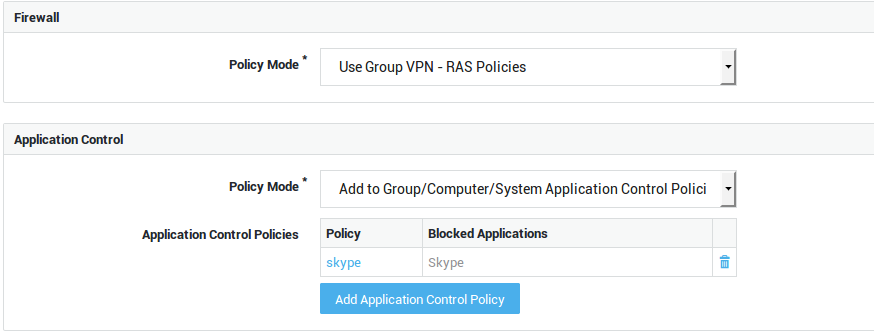
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
Use Group Firewall Policies |
Select this option if you wish to apply the same firewall policies for VPN use as defined in the user’s group. |
Add to Group Firewall Policies |
Select this option to add specific policies for VPN use, in addition to the user’s group firewall policies. |
Overrule Groups Firewall Policies |
Select this option to overrule the group firewall configuration and specify unique policies for the user. |
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
Use group application control policies |
Only enforce the policies as configured for the user’s group. |
Add to group application control policies |
Enforce the policies as configured for the user’s group and the policies that are specified in the user profile. |
Overrule group application control policies |
Only policies configured at the user, computer and system levels are enforced. Group policies are not enforced. |
Overrule Group / Computer / System Application Control Policies |
Only the application control policies configured at the user level are enforced. |
User Authentication¶
-
Go to Authentication > Services.
-
Select SSTP VPN.
-
Select the appropriate authentication policy.

AXS Guard Service |
Authentication Policy |
|---|---|
PPTP / SSTP / L2TP |
|
Viewing Active Sessions¶
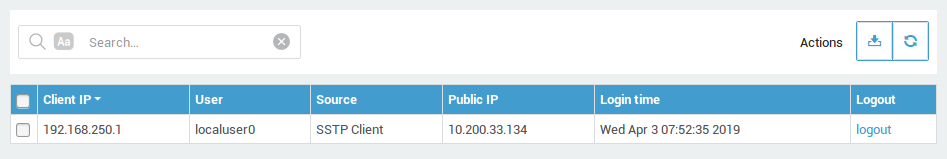
Go to Authentication > Status > Authenticated Users and select
Firewall, Proxy and VPN to view users who are currently authenticated.
Via this page you can also remotely log out users by clicking on the
logout link as shown below.
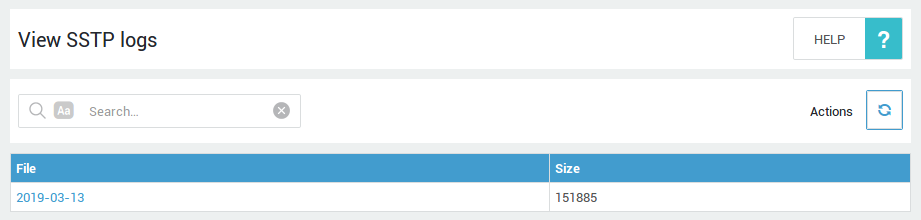
Logging¶
-
Go to VPN > SSTP > Logs.
-
Click on the appropriate date.
Windows Client Configuration Example¶
Configuration Overview¶
In this chapter, we explain how to configure your Windows SSTP client. In the following example, we will be using a server certificate signed by the AXS Guard CA and two-factor authentication (password + OATH token). Following is an overview of the configuration steps:
-
Export the AXS Guard CA certificate.
-
Add this CA as a trusted root CA on the Windows client(s).
-
Set up a new SSTP connection on Windows.
Importing the AXS Guard Root CA¶
Skip this step if the AXS Guard SSTP server has been configured with a certificate issued by a public CA.
-
Log in to Windows as a system administrator.
-
Start a browser and log in to your AXS Guard appliance.
-
Go to PKI > Built-in CA and click on the "Export CA" button.
-
Install the CA certificate in Windows by double-clicking on the downloaded certificate file.
-
Select the following store location:
Local Machine.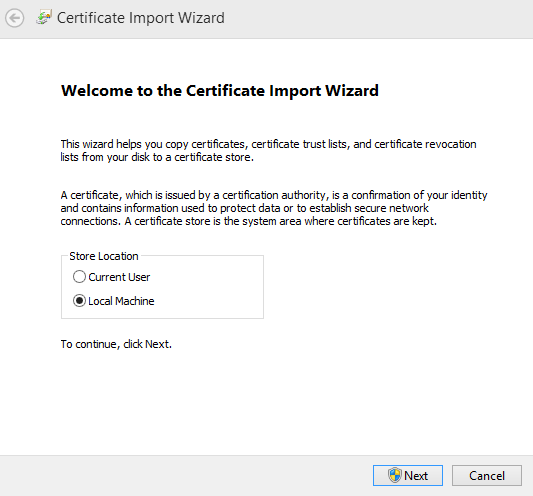
-
Install the certificate in the
Trusted Root Certification Authoritiesstore.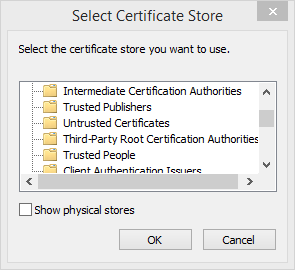
Setting up a Connection¶
-
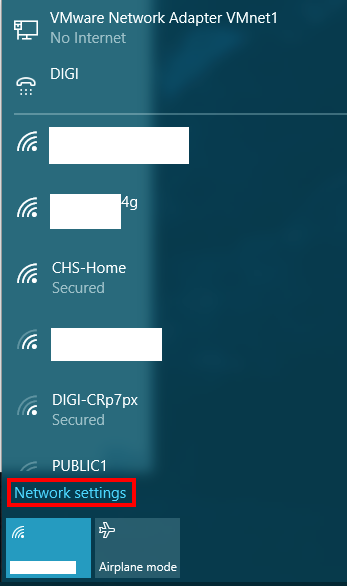
Click on the Network icon(tray icon) and then click on the Network Settings link.
-
Click on
+ Add a VPN connection.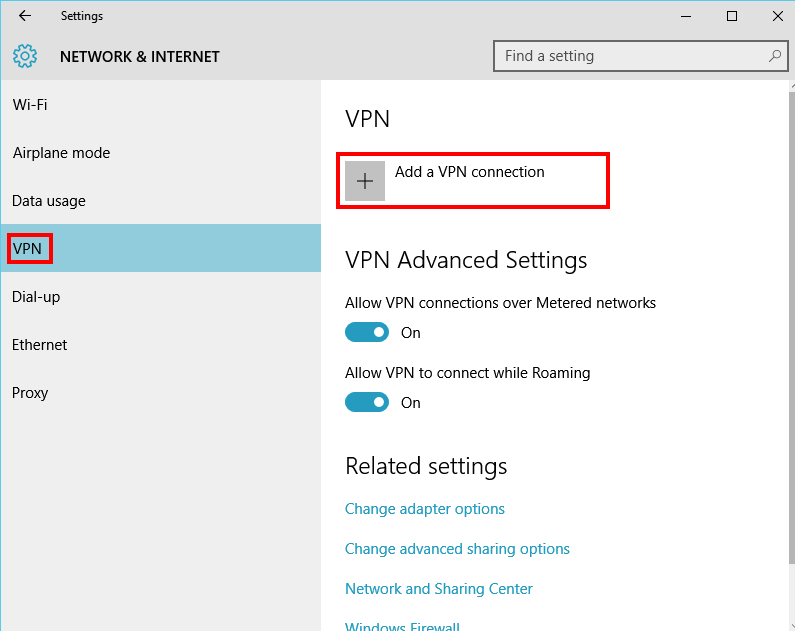
-
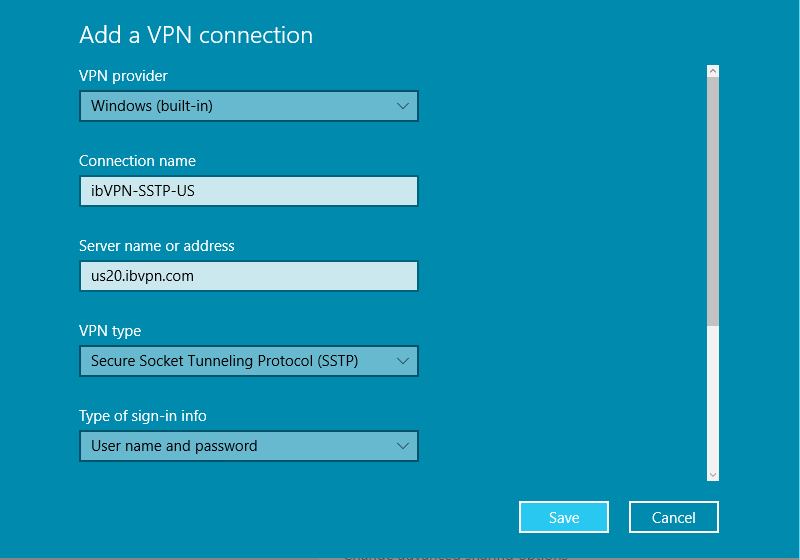
Input the following:
-
Choose a Connection name: ex: ibVPN-SSTP-US
-
Input the server name (make sure you input the server name which matches the CN of the SSTP server certificate and not the IP address)
-
Choose
Username and passwordfor Type of sign-in info. -
Do not input your VPN password, as we are using OATH authentication (one-time passwords generated by an app on the user’s smartphone).
-
Click Save.
-
-
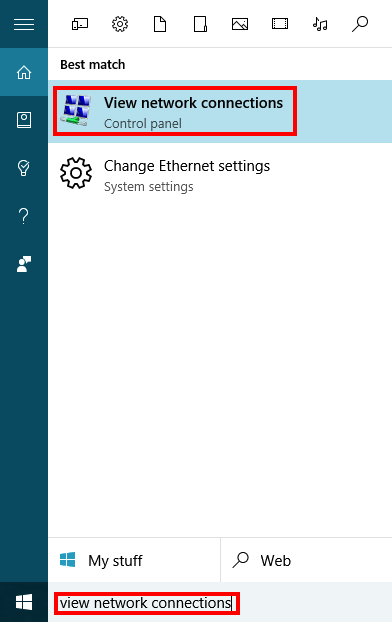
Search for "view network connections." Then click on the icon highlighted in the picture below.
-
Click on the newly added VPN connection (ibVPN-SSTP-US in this example), and then click on
Properties.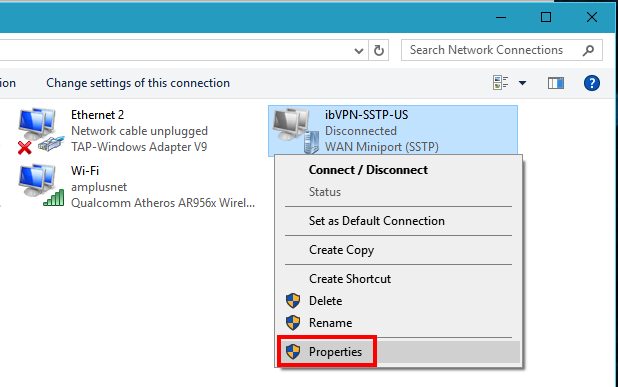
-
Click on the
Securitytab and selectSecure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP)andRequire encryption, then select the desired protocol. Only the following protocols are supported:-
EAP-MSCHAP v2 (Windows default)
-
Microsoft CHAP Version 2 (MS-CHAP v2)
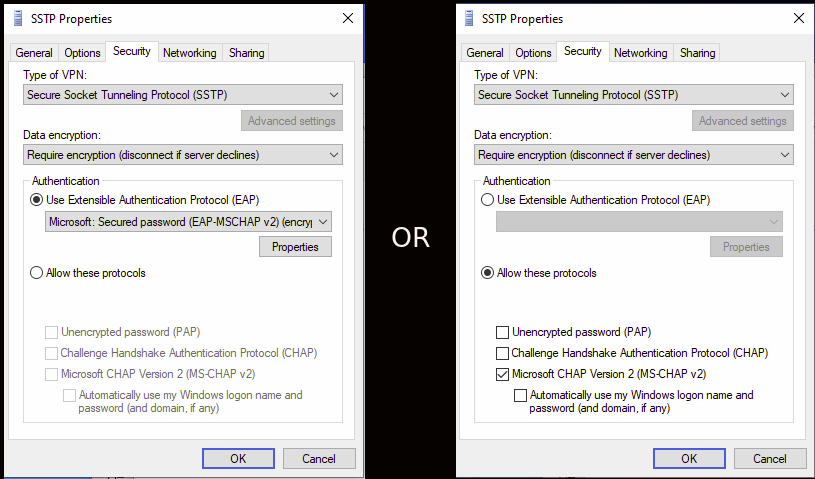
-
-
Click on the
Network Connectionsicon. -
Next, select the newly created SSTP connection (ibVPN-SSTP-US in this example).
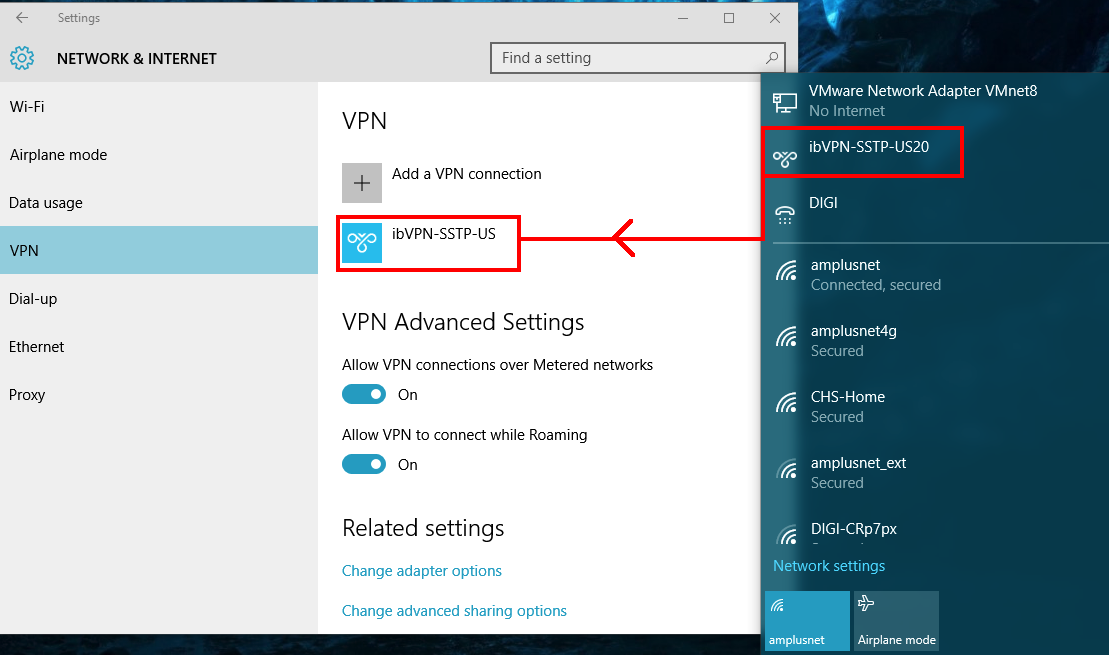
-
Click on the SSTP VPN adapter (ibVPN-SSTP-US in the example).
-
Then click
Connect.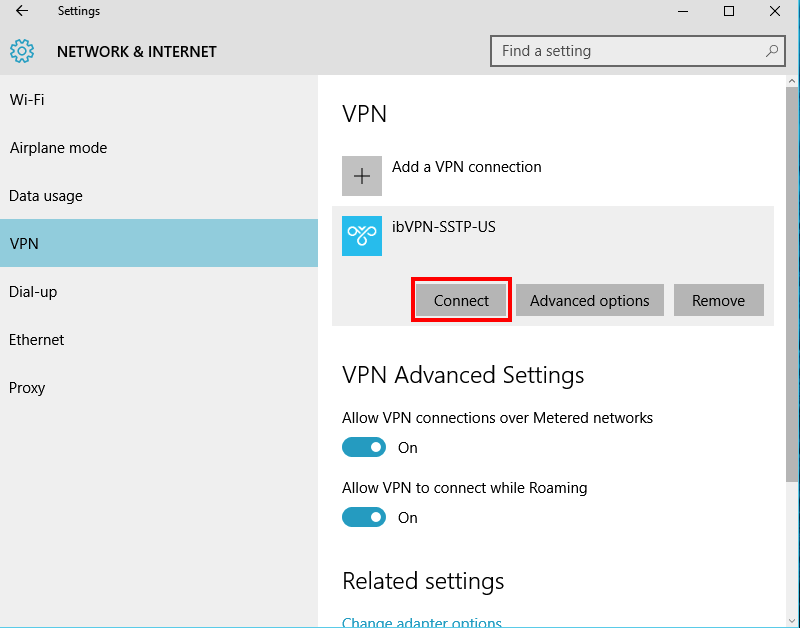
-
Input your username and password followed by the one-time password generated with your OATH token (smartphone).
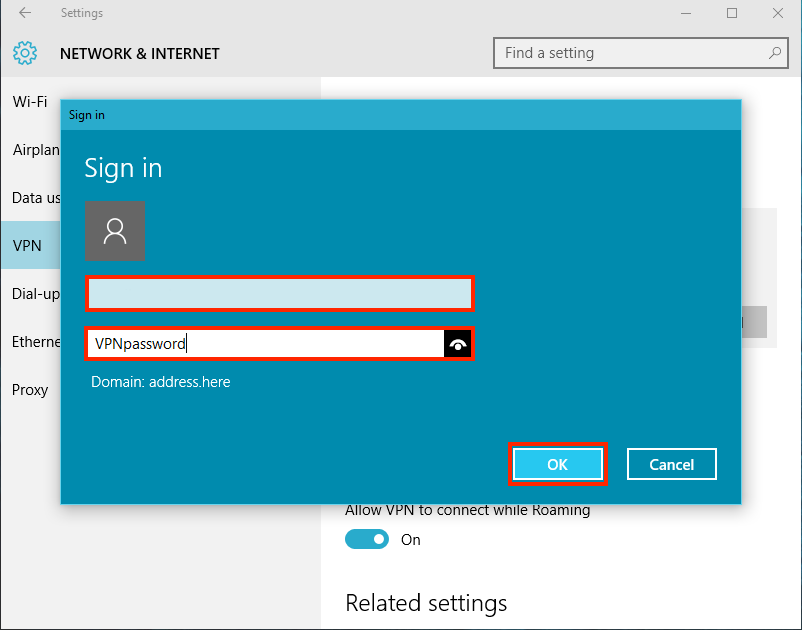
Important
Note that Internet-style login names, e.g. user@example.com, cannot be used to log in to the AXS Guard SSTP server.
You are now connected via SSTP VPN. You can access your corporate network resources and check your IP address here.
Setting up Routing¶
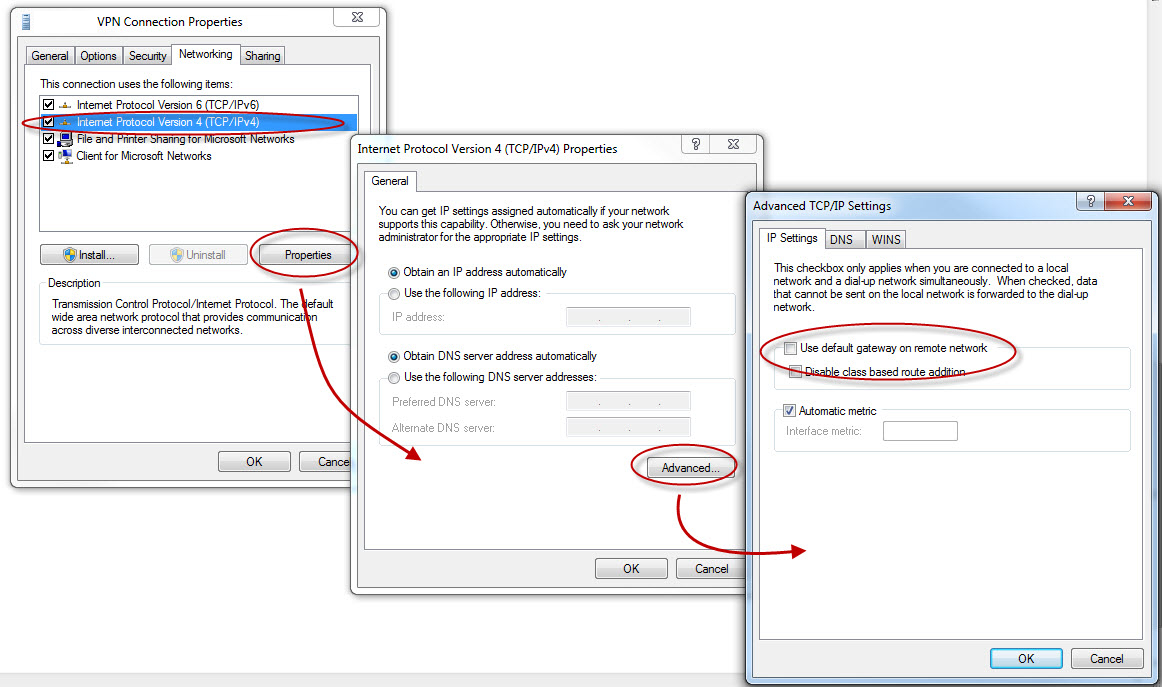
The Windows SSTP client routes all network traffic through the VPN connection by default.
This behavior can be changed by modifying the properties of the VPN
connection. In the Networking tab, select the
Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) properties, then click on the
Advanced button and untick Use default gateway on remote network.
This will prevent the VPN from changing the default route when a connection is made.
Troubleshooting¶
Known issues with private Certificate Authorities
After a certain time, the certificate you placed in the “Trusted Root Certification Authorities” store as part of the instructions just disappears and will cause the client to throw an error.
It’s easy enough to put it back, but it will eventually get removed again, because of the Automatic Third-Party CA Updates process that runs on Windows. This process goes to Windows Update periodically to get an updated list of trusted third-party certificate authorities and if it finds any certificates not present in the list they get deleted.
There are basically two options to fix this:
-
Option 1: Stop using self-signed certificates. Instead of using a self-signed certificate, use a certificate issued by a trusted third-party CA, e.g. LetsEncrypt.
-
Option 2: Turn off automated Third-Party CA Updates. Note that this is not recommended from a security perspective.
In an Active Directory domain, this can be achieved with a group policy. On local machines there is a policy under Computer Configuration / Administrative Templates / System / Internet Communication Management / Internet Communication Settings. There you must enable “Turn off Automatic Root Certificate Update”.
Known issues with VPN clients where the SSO authentication tool is installed
The Single Sign-On (SSO) tool is designed to transparently authenticate users against the AXS Guard authentication server in the secure LAN.
When a VPN connection is established by a client where this tool is installed, it may automatically attempt to log in the user over the VPN connection. As a result, the user will be logged out of the authenticated VPN session.
The easiest way to block the SSO tool from automatically logging in a user who is already authenticated over a VPN connection is by configuring a static firewall policy as explained in the document "Blocking SSO to prevent VPN disconnect issues", which can be found in the knowledge base section of the AXS Guard documentation site.
Client authentication fails (there was an internal authentication error).

Whereas most of the Unix and POSIX world uses UTF-8 for text representation, Windows 10 and 11 currently still use UTF-16LE. By design, the Microsoft Windows SSTP client is not capable of transcoding UTF-8 to UTF-16LE. This means that users will get an error when using certain special characters in their password, e.g.
Original password (UTF-8):
$ cat sstp_password.txt password€
Transcoded password (UTF-16LE):
$ iconv -f UTF-8 -t UTF16LE sstp_password.txt password�
Support¶
If you encounter a problem¶
If you encounter a problem with AXS Guard, follow the steps below:
-
Check the troubleshooting section of the feature-specific manual.
-
Check the knowledge base on this site for information about special configurations.
-
If no solution is available in any of the above sources, contact your AXS Guard vendor.
Contact Information¶
(+32) 15-504-400
support@axsguard.com